Scan patterns during scene viewing predict individual differences in clinical traits in a normative sample
Abstract
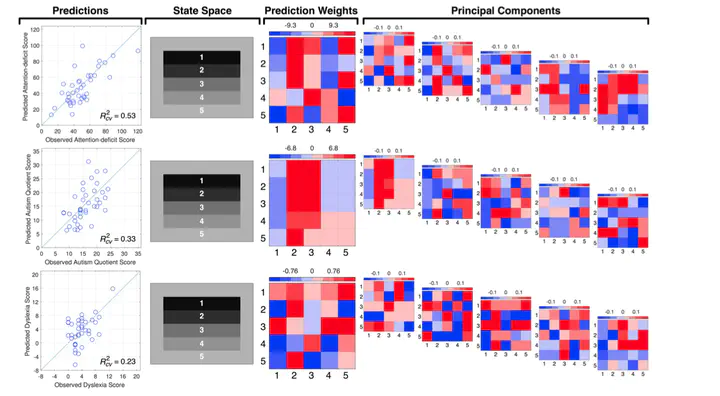
The relationship between viewer individual differences and gaze control has been largely neglected in the scene perception literature. Recently we have shown a robust association between individual differences in viewer cognitive capacity and scan patterns during scene viewing. These findings suggest other viewer individual differences may also be associated with scene gaze control. Here we expand our findings to quantify the relationship between individual differences in clinical traits and scene viewing behavior in a normative sample. The present study used Successor Representation Scanpath Analysis (SRSA) to quantify the strength of the association between individual differences in scan patterns during real-world scene viewing and individual differences in viewer attention-deficit disorder, autism spectrum disorder, and dyslexia scores. The SRSA results revealed individual differences in vertical scan patterns that explained more than half of the variance in attention-deficit scores, a third of the variance in autism quotient scores, and about a quarter of the variance in dyslexia scores. These results suggest that individual differences in attention-deficit disorder, autism spectrum disorder, and dyslexia scores are most strongly associated with vertical scanning behaviors when viewing real-world scenes. More importantly, our results suggest scene scan patterns have promise as potential diagnostic tools and provide insight into the types of vertical scan patterns that are most diagnostic.