A novel method for analyzing sequential eye movements reveals strategic influence on Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices
Abstract
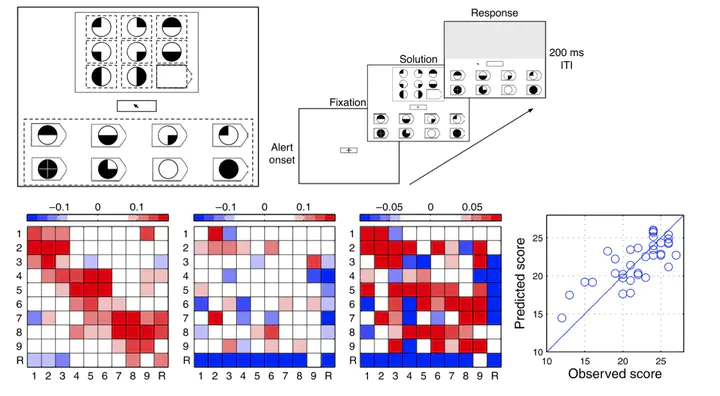
Eye movements are an important data source in vision science. However, the vast majority of eye movement studies ignore sequential information in the data and utilize only first-order statistics. Here, we present a novel application of a temporal-difference learning algorithm to construct a scanpath successor representation (SR; P. Dayan, 1993) that captures statistical regularities in temporally extended eye movement sequences. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the scanpath SR on eye movement data from participants solving items from Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices Test. Analysis of the SRs revealed individual differences in scanning patterns captured by two principal components that predicted individual Raven scores much better than existing methods. These scanpath SR components were highly interpretable and provided new insight into the role of strategic processing on the Raven test. The success of the scanpath SR in terms of prediction and interpretability suggests that this method could prove useful in a much broader context.